Arc lamps hold a unique place in the history of artificial lighting. Long before LED and modern electric bulbs became common, arc lamps introduced the idea of powerful, controlled illumination using electrical discharge.
From early scientific experiments to street lighting, cinema projection, and modern interior design, arc lamps have evolved while maintaining their core principle. This guide explores what arc lamps are, how they work, where they are used, and why their legacy still matters today.
Table of Contents
What Is an Arc Lamp
An arc lamp produces light by creating an electrical arc between two electrodes. When electricity passes through the gap, the surrounding gas becomes ionized and emits an intense, bright light.
Unlike traditional bulbs that rely on filaments, arc lamps generate illumination through electrical discharge. This allows them to produce significantly higher brightness and a more focused beam.
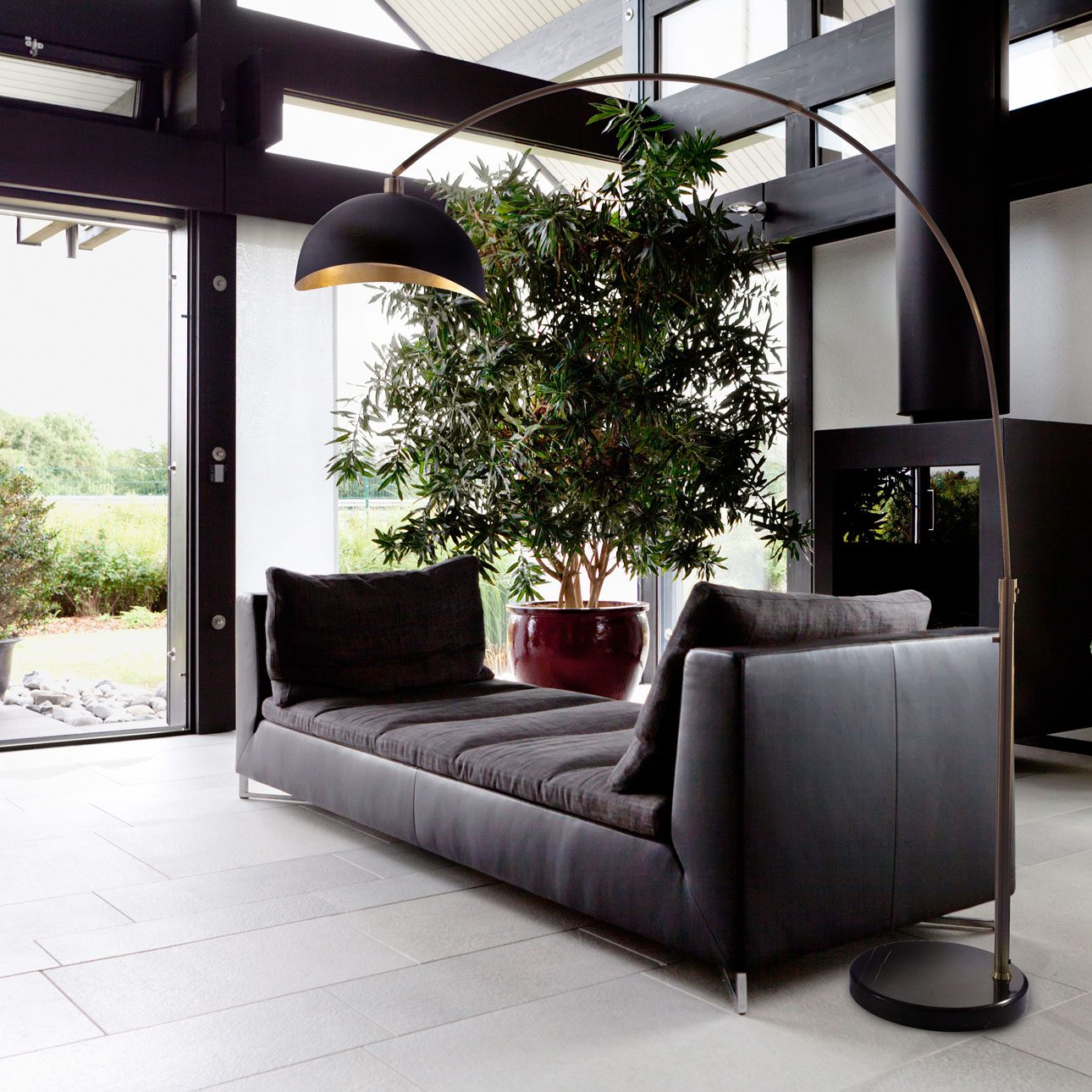
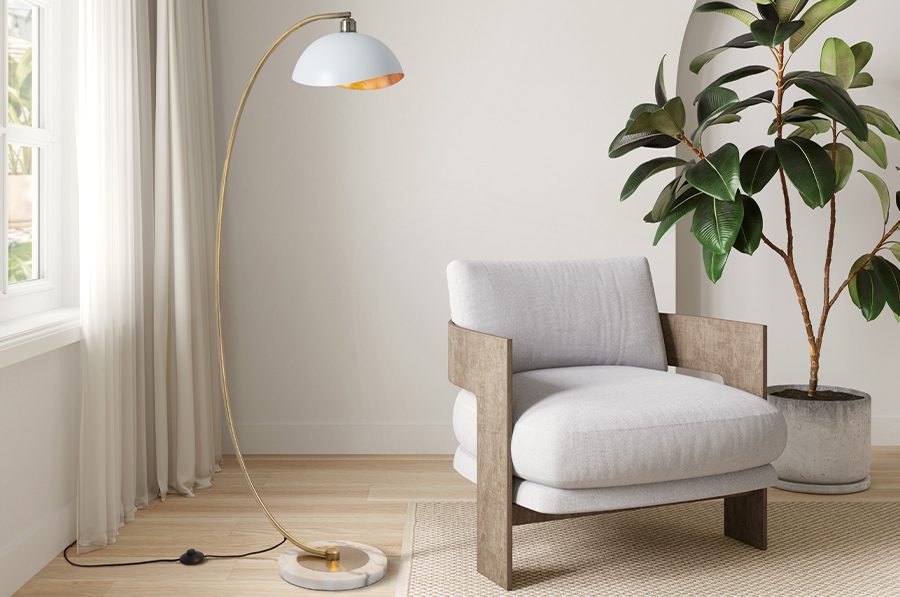
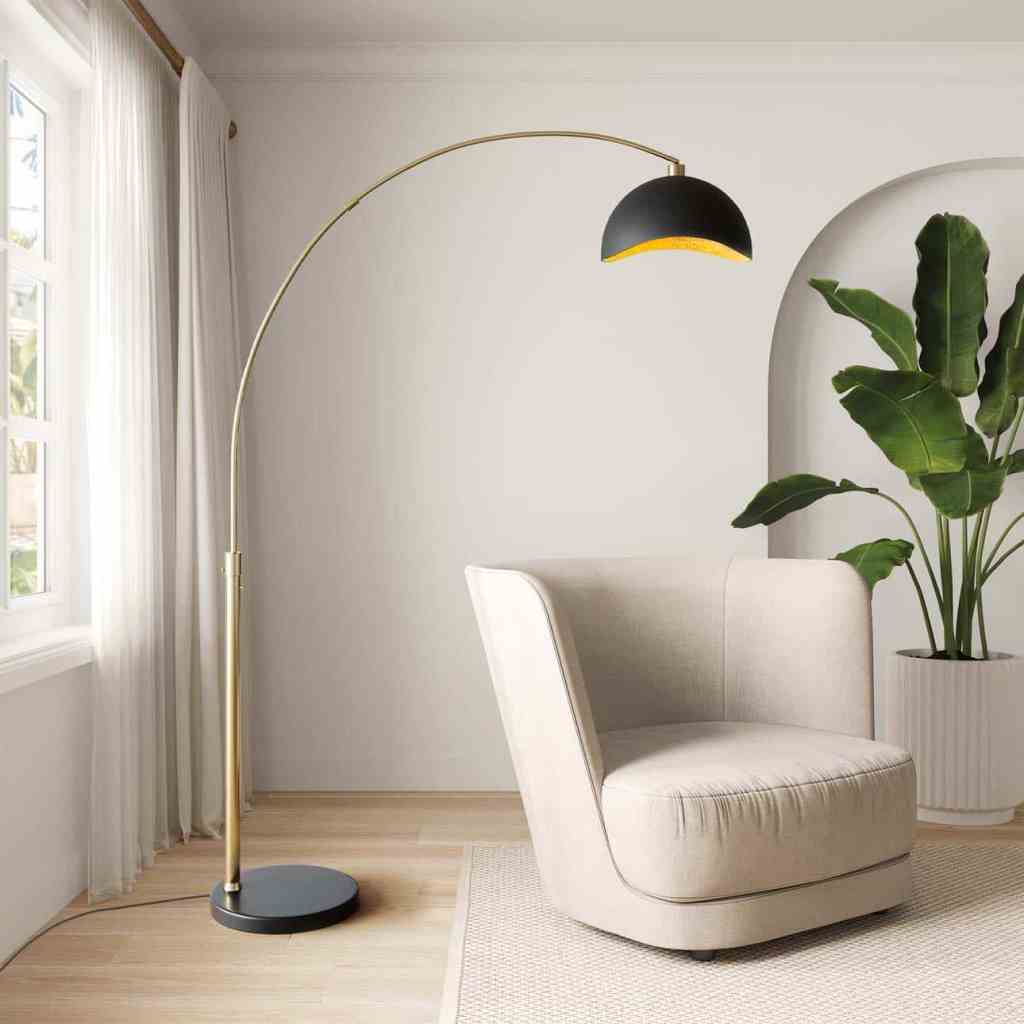
Today, the term arc lamp can describe both industrial lighting systems and decorative arc floor lamps used in modern interiors.
The Origins and History of Arc Lamps
The arc lamp was first demonstrated in the early nineteenth century by Sir Humphry Davy. His experiments showed that electricity could create sustained light through an arc between carbon electrodes.
Key historical milestones include:
- Early 1800s: First successful arc light demonstrations
- Late 1800s: Arc lamps used in street lighting across major cities
- Early twentieth century: Adoption in theaters and film projection
- Modern era: Continued use in specialized industries and design lighting
For decades, arc lamps were the brightest artificial light source available. Their ability to illuminate large areas made them essential before incandescent and fluorescent technologies matured.
How Arc Lamps Work
The operation of an arc lamp relies on a simple but powerful process:
- Electrical current flows between two electrodes
- The air or gas between them becomes extremely hot
- Ionized gas emits intense white light
- The arc remains stable through controlled voltage
This process creates a strong and concentrated beam, which is why arc lamps excel in applications requiring high brightness and precision.
Types of Arc Lamps
Arc lamps vary based on their application and environment.
Decorative Arc Floor Lamps
These are commonly used in living rooms, bedrooms, reading areas, and home offices. They provide overhead illumination without ceiling installation and serve as sculptural design elements.
Industrial and Technical Arc Lamps
These include mercury arc lamps and other high intensity discharge systems used in street lighting, projectors, and scientific equipment.
Each type follows the same lighting principle but differs in scale, materials, and intended use.
Advantages of Arc Lamps
Arc lamps offer benefits that many lighting systems cannot match.
Long Lifespan
Arc lamps typically last much longer than incandescent bulbs and often outlast fluorescent lighting. Fewer replacements reduce long term costs and maintenance effort.
High Brightness Output
The intense light produced by arc lamps allows fewer fixtures to illuminate large spaces. This makes them ideal for wide areas and task specific lighting.
Strong Energy Performance
Arc lamps generate a high amount of light per watt. This efficiency translates to lower operating costs in large scale or continuous use environments.

Common Applications of Arc Lamps
Movie Projectors
Arc lamps played a critical role in cinema development. Their steady and powerful beam made film projection possible long before digital systems.
Searchlights
In rescue operations and security settings, arc lamps provide long range visibility. Their focused beam can scan wide areas efficiently.
Street Lighting
Historically, arc lamps improved nighttime safety by illuminating roads and sidewalks. Their brightness reduced accidents and increased public visibility.
Arc Lamps Compared to Other Lighting Sources
Arc Lamps vs Incandescent Lighting
Arc lamps last longer, consume less energy, and produce significantly more light. Incandescent bulbs generate more heat and require frequent replacement.
Arc Lamps vs Fluorescent Lighting
Arc lamps offer focused illumination and do not rely on mercury. Fluorescent lighting works better for ambient coverage but has disposal limitations.
Arc Lamps vs LED Lighting
LEDs provide versatility and compact design options. Arc lamps deliver higher intensity and whiter light for specific applications. Both are energy efficient, though LEDs dominate general household use.
Maintenance and Care for Arc Lamps
Proper maintenance ensures consistent performance and long service life.
Cleaning
Dust and residue can reduce light output. Always power off the lamp and clean surfaces with a soft cloth and manufacturer approved solutions.
Lamp Replacement
When replacement is required, follow safety guidelines carefully. Handle components with gloves and dispose of used lamps responsibly.
Power Supply Inspection
Stable voltage is essential for arc lamp performance. Regularly inspect cords, connections, and power units for wear or instability.
Why Arc Lamps Still Matter Today
While modern lighting technology continues to evolve, arc lamps remain relevant in specialized applications and design focused interiors. Their intense brightness, historical significance, and distinctive form keep them in use across industries and homes.
From scientific innovation to modern living spaces, arc lamps represent a lasting chapter in lighting history.